1601. GCD of two numbers
Find the GCD (greatest common divisor) of two non-negative integers.
Input. Two integers a and
b (a, b ≤ 2 * 109).
Output. Print the GCD of numbers a and b.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
42 24 |
6 |
SOLUTION
number theory - GCD
Algorithm analysis
The greatest common divisor (gcd)
of two integers is defined as the largest non-negative integer that divides both
of these integers. For example, gcd(8, 12) = 4.
It is known that
gcd(0, x) = |x| (the absolute value of x),
because |x| is the largest non-negative
integer that divides 0 and x. For
example, gcd(-6, 0) = 6, gcd(0, 5) = 5.
To find the gcd
of two numbers, you can use an iterative algorithm: subtract the smaller number
from the larger one. When one of the numbers becomes 0, the other one becomes
the gcd. For example, gcd(10, 24) = gcd(10, 14) = gcd(10, 4) = gcd(6, 4) =
gcd(2, 4) = gcd(2, 2) = gcd(2, 0) = 2.
If instead of the
“subtraction” operation, you use the “modulo” operation, the calculations will proceed
significantly faster.
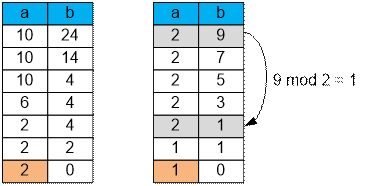
For example, to
find GCD (1, 109) uning subtraction,
you would need to perform 109 operations. Using the modulo operation, only one action is required.
The GCD of two numbers can
be computed using the formula:
 ,
,
or the same as
GCD(a, b) = ![]()
The iterative
implementation is based on the idea presented in the final recurrence relation:
while
(b > 0) :
compute
a = a % b;
swap
the contents of variables a and b;
Algorithm implementation
The gcd function
computes the GCD of two numbers.
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (a == 0) return b;
if (b == 0) return a;
if (a >=
b) return gcd(a % b, b);
return gcd(a,
b % a);
}
The main part of the
program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
Compute and print the GCD
of two numbers.
d = gcd(a,b);
printf("%d\n",d);
Algorithm implementation – simplified recursion
The gcd
function computes the GCD of two numbers.
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return (!b) ?
a : gcd(b,a % b);
}
The main part of the
program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
Compute and print the GCD
of two numbers.
d = gcd(a,b);
printf("%d\n",d);
Algorithm implementation – iterative
The gcd
function computes the GCD of two numbers.
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
while (b >
0)
{
a = a % b;
int temp = a; a = b; b = temp;
}
return a;
}
The main part of the
program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
Compute and print the GCD
of two numbers.
d = gcd(a,b);
printf("%d\n",d);
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (a ==
0) return b;
if (b ==
0) return a;
if (a
>= b) return gcd(a % b, b);
return gcd(a, b % a);
}
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int a = con.nextInt();
int b = con.nextInt();
int res = gcd(a, b);
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation – recursion
The gcd
function computes the GCD of two numbers.
def gcd(a, b):
if a == 0: return b
if b == 0: return a
if a > b: return gcd(a %
b, b)
return gcd(a, b
% a)
The main part of the
program. Read the input data.
a, b = map(int, input().split())
Compute and print the GCD
of two numbers.
print(gcd(a, b))
Python implementation – gcd
To compute the greatest common divisor
(GCD) of two numbers, let’s use the gcd function built into the
Python language.
import math
Read the input data.
a, b = map(int, input().split())
Compute and print the GCD
of two numbers.
print(math.gcd(a, b))